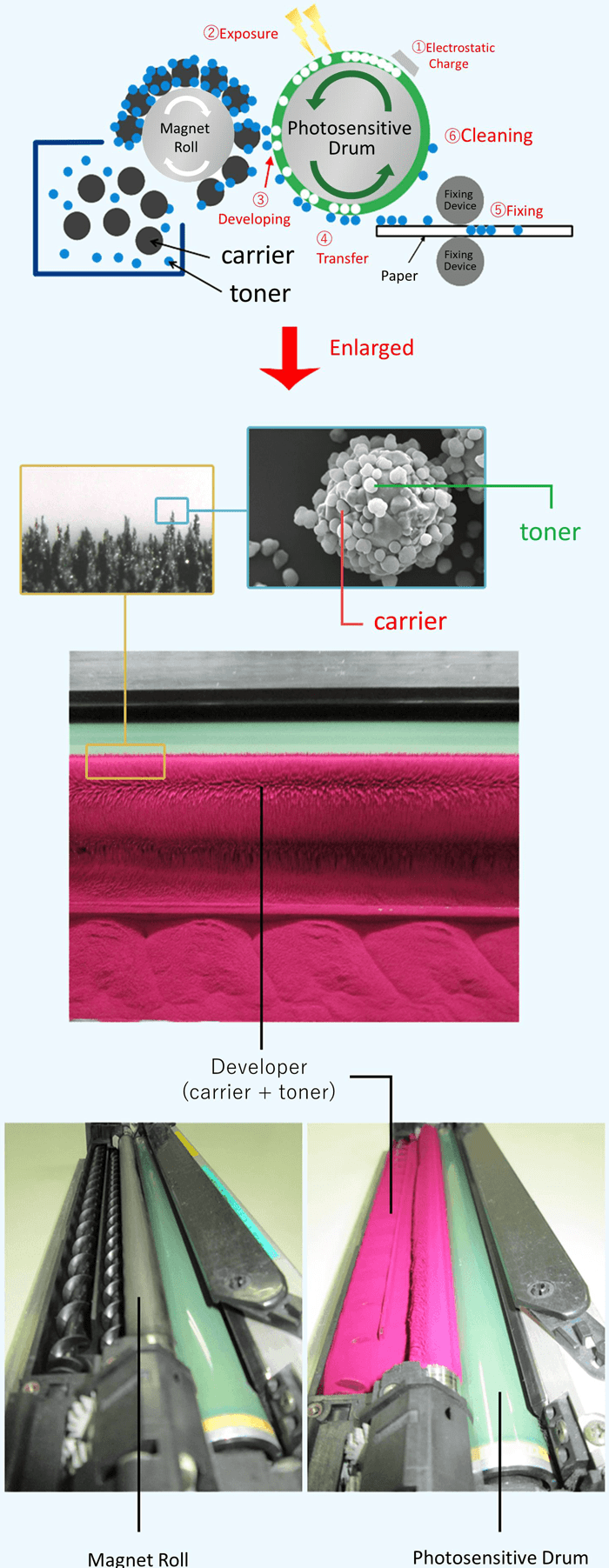
The Function of Carriers
The electrophotographic carrier used in two-component developers is a magnetic material used to form the toner image on a photoreceptor drum.
The carrier is mixed and agitated with the toner in a developing box filled with developer to give the toner particles the desired electric charge.
The carrier and toner form a magnetic brush on the magnet roll, which transports the charged toner particles to the surface of the photoreceptor drum.
The carrier particles remaining on the magnet roll are returned to the developing box, mixed and agitated with new toner particles, and used repeatedly within a given time frame.

The electrophotographic carrier material transfers toner particles to the photoreceptor drum, for which it earns the name “carrier.” Toner particles thus transported to the surface of the photoreceptor drum are transferred onto paper when they pass through the fusing unit, being fused and fixed to the paper by heat and pressure.
electrophotographic system two-component developer system outline
Carrier Composition
Steel flat iron powders were initially used as the carrier material, with an average particle size of 50 to 150 µm. Later, sponge iron powders were used, from irregular to spherical, followed by atomized iron powders. Currently, to meet market demands for high image quality, durability, and reliability, resin-coated ferrite carriers have become mainstream. They use a coated ferrite powder (core material) with an average grain size of 20 to 50 µm and a surface coating of organic resin.
In two-component developers, the properties of the electrophotographic carrier must be stable to maintain the many characteristics indicative of image quality (image density, resolution, gradation, etc.).
Specifically, the carrier must exhibit the specified values from the initial stage forward and remain stable during printing and through changes in the external environment.
Core Material
Although Cu-Zn (copper-zinc) ferrite was the main type being used for ferrite powder, we developed EF (environmentally friendly) ferrite, which does not contain heavy metals, to meet the market demand for lower environmental impact. EF ferrite core materials are the most prevalent in use today.
Important properties for the core material are its magnetization, which helps form the magnetic brush, and its specific surface area, which helps transport the toner.
Resin Coating
We use a range of organic resins to coat the surface of the core material, depending on the required functions and target properties.
The resins are typically silicone resins and acrylic resins. In recent years, various materials have been added to these base resins.
Additives are used not only to adjust the electrical resistance and charging properties, which are key properties, but also to improve adhesion between the core material and the base resin, to improve the abrasion resistance of the base resin, and to suppress fluctuations in developer properties due to environmental variation.
Resin-coated ferrite carrier
(left: electron micrograph; right: schematic diagram)


Carrier Types
The table below shows the main types and characteristics of our electrophotographic carriers.
Core Materials
Ferrite cores of various compositions are available.
For our EF types (Mn-Mg-Sr-Fe), saturation magnetization can be adjusted as desired within the range shown in the table.
The surface properties of the core material can also be adjusted from wrinkled to smooth as shown in the figure below.
Ferrite Core Material for Carriers for Electrophotographic Developer
| Classification | Saturation magnetization | Average grain size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | Composition | Type | (A㎡/kg) | (㎛) |
| F type | Cu-Zn-Fe | Soft ferrite | 60~70 | 50~80 |
| EF type | Mn-Mg-Sr-Fe | Soft ferrite | 50~75 | 20~100 |
| Mn-Mg-Zr-Fe | Soft ferrite | 65~85 | 20~100 | |
| MF type | Mn-Fe | Soft ferrite | 90~97 | 50~100 |
Changes in ferrite surface properties (example)


Resin Coating
There are three main types of resin coating—silicone, acrylic, and fluorine.
Adjustments can be made by request in the amount of coating and type of additives used (charge control agents, conductivity control agents, adhesion enhancers, etc.)
Electrophotographic Carrier Product Characteristics (Examples)
The products listed in the table below are only representative examples. We can supply electrophotographic carriers with various characteristics by selecting and combining the following properties and specifications to meet the customer’s objectives.
- Ferrite core composition
- Ferrite core average grain size
- Resin coating use/no use
- Resin coating material type
If you have any questions about these materials such as their merits/demerits or detailed characteristics, feel free to contact us.
Electrophotographic Carrier Product Characteristics (Examples)
| Product | Composition | Shape | Resin coating | Saturation magnetization (Am2/kg) |
Average grain size (㎛) |
Apparent density (g/cm3) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use (yes/no) | Type | ||||||
| F-50 | Cu-Zn-Fe | Spherical | No | - | 60~70 | 50 | 2.3~2.7 |
| EF-60 | Mn-Mg-Sr-Fe | Spherical | No | - | 50~75 | 60 | 2.3~2.6 |
| EF-50 | 50 | 2.2~2.5 | |||||
| EF-35 | 35 | 2.0~2.4 | |||||
| EF96 | Yes | silicone type | 35 | 2.0~2.4 | |||
| EF46 | acrylic type | 35 | 2.1~2.5 | ||||
| EF83 | 35 | 2.1~2.5 | |||||
| MF-80 | Mn-Fe | Spherical | No | - | 90~97 | 80 | 2.4~2.7 |
| MF-60 | 60 | 2.4~2.7 | |||||
* The above values are representative values, not standard values.
Electron Micrograph of Resin-coated Ferrite Carrier for Electrophotography (Example)


If you have any questions about these materials such as their merits/demerits or detailed characteristics, feel free to contact us.
